Design Thinking a “Human-centered” approach for innovation
January 20, 2023 | Read Time : 3 mins
Table of Contents
What is Design Thinking?
Design Thinking is a human-centered approach to problem-solving. It helps designers create solutions that address real user problems.
Popular Design Thinking Frameworks:
Heart, head, and hand
Before engaging in cognitive processing for ideation, evaluation, and diving into the manual fabrication of the practical parts, the method strongly emphasizes vision, need, emotion, and feeling.
The Design Thinking process has 5 phases, and they are as follows:
- Empathize — During the empathize phase, the goal is to understand the user’s needs and how users think and feel. We can get detailed information about who our users are and the challenges they are facing.
- Define — The next step in the design phase is defining the user problem once we gather the required information about the user’s needs and wants.
- Ideate — The goal of the ideate phase is to think of as many possible ideas and solutions to the user’s problems.
- Prototype — After getting an idea of how to solve the problem, we enter the prototype phase. The prototype is an initial model of a product that demonstrates its functionality
- Test — During the test phase, users provide feedback about the product design before the product is developed by the engineering team and launched to the public.
DeepDive
The steps in the deep dive process are as follows:
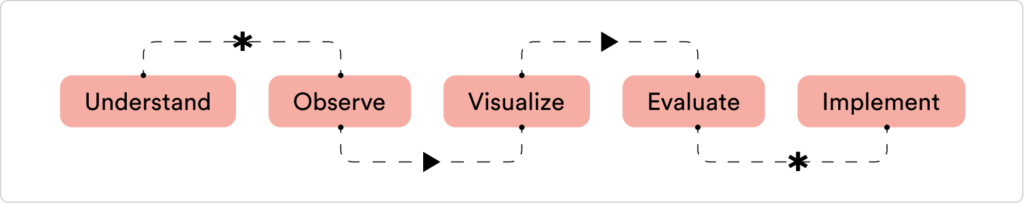
The Design Council of the UK: 4D’s
The Design Council of the UK has settled on the 4D’s, they are as follows:
- Discover
- Define
- Develop
- Deliver
Frog Design
The Explore, Converg, and Support strategy of Frog Design suggests focusing on more than just the finished product and maintaining a relationship with its customers even after the project completion.
Luma System
This method teaches that innovation and human-centered design have their expression. It allows for remixing many processes using the procedures specific to your needs.
Understanding the importance of Design Thinking in enabling innovation
Design Thinking need not be understood as only an approach to addressing a predetermined set of issues. It is a concept that may be used when creativity or unconventional thinking is required. Design Thinking can also be used with other approaches, business plans, models for social innovation, and managerial techniques.
“It’s about human-centered innovation”
Challenges of innovation
An innovation process must deliver superior solutions, lower risks and costs, and employee buy-in. However, companies frequently encounter unexpected challenges
Smarter Solutions
Bringing diverse voices together and incorporating user-driven criteria creates improved solutions. But this can be difficult if people have opposing views that deteriorate into unhealthy debates.
Minimum Risks & Costs
Innovators must be willing to let go of high-risk ideas. Taking quick, iterative actions to test the market effectiveness is an excellent strategy for innovation. This approach may lead to an inexpensive failure, minimum investment, and a more significant learning experience.
Employee Commitment
Without the commitment of a company’s employees, innovation won’t prosper.
Engaging them in the process of ideas is the surest way to win their support.
What problems can Design Thinking solve?
Design Thinking can be utilized to solve a variety of problems and is most effective for fostering creativity in the following contexts:
- Human-centered innovation
- Shifting markets and behaviors
- Re-inventing business models
- Complex unsolved societal challenges
- Quality of life
- Entrepreneurial initiatives
- Educational advances
- Medical breakthroughs
How Design Thinking can power innovation teams?
Organized processes help people stay on task and reduce the urge to delay or spend excessive time solving a problem.
Instead of gathering and analyzing data, these methods examine what creates a meaningful customer journey.
Design thinking adapts a unique approach, encouraging the inventor to live the customer’s experience to uncover hidden demands.
One of the most effective ways to make sense is to select only the most critical data.
Diverse teams can have more collaborative and creative talks about the design criteria that an ideal solution should have when they focus less on the limitations and more on the possibilities.
After thoroughly understanding customer needs, innovators can continue to find and help determine specific solutions that meet the criteria.
Importance must be given to establishing a dialogue regarding potential solutions, careful planning on who will participate, what challenges will occur in innovation, and how the ideas will structure the conversation.
Design thinking frames the conversation as a study into what ideas of the world must be valid for a concept to be practical.
The prototyping process should be about users’ iterative experiences with a work in progress.
The three pillars of Design Thinking are involvement, conversation, and learning. It generates a broad commitment to change by integrating customers and other stakeholders in the problem-identification process and the development of solutions.
Design thinking also facilitates collaboration among innovators on what is crucial to the outcome at each stage by giving the innovation process a proper structure.



