Understanding Lean Product Management and How It’s Applied to Product Design
August 8, 2023 | Read Time : 3 mins
Table of Contents
In the fast-paced world of product design, efficiency and agility are paramount. Traditional project management approaches often fall short when adapting to rapidly changing user needs and market dynamics. That’s where Lean Product Management comes into play.
By embracing Lean principles, product teams can foster a culture of continuous improvement, optimize resources, and deliver high-value products that resonate with users. We will explore the core tenets of Lean Product Management and examine how they are applied to product design.
What is Lean Product Management?
Lean Product Management is a methodology that applies Lean principles to product development. It focuses on delivering value to customers while minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency. At its core, Lean Product Management is driven by the relentless pursuit of continuous improvement and creating products that effectively meet user needs.
Lean Product Management strongly emphasizes validated learning, where user data and feedback play a central role in decision-making. It encourages cross-functional collaboration, bringing together designers, developers, and product managers to leverage their unique perspectives and expertise. Adopting an iterative and adaptive approach, Lean Product Management allows teams to quickly validate assumptions, make informed decisions, and deliver tangible products.
The Foundations of Lean Product Management
Lean Thinking
- Eliminating waste: Lean Product Management aims to identify and eliminate wasteful activities, such as overproduction, excess inventory, unnecessary processes, and non-value-added features.
- Continuous improvement: It encourages a culture of Kaizen, where teams constantly seek ways to improve efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction.
- Respect for people: Lean emphasizes empowering and involving team members, valuing their expertise, and fostering collaboration and open communication.
Agile Development
- Iterative and incremental approach: Agile methodologies, such as Scrum or Kanban, promote iterative development cycles with frequent feedback loops, allowing teams to adapt quickly to changing requirements.
- Cross-functional collaboration: Agile teams consist of members with diverse skills, encouraging close collaboration between developers, designers, product managers, and other stakeholders.
- Adaptive planning: Agile embraces the notion that plans will change, emphasizing flexibility and responsiveness to market feedback and user needs.
Applying Lean Principles to Product Design
- Validated Learning: Lean Product Management encourages teams to gather data and insights from real users as early as possible to inform decision-making and minimize assumptions. User research methods such as interviews, surveys, usability testing, and A/B testing are employed to gain actionable feedback and validate hypotheses.
- Minimum Viable Product (MVP): Developing an MVP allows teams to deliver a product with the minimum features required to address the core user needs and test its viability in the market. By collecting user feedback and usage data on the MVP, teams can refine and iterate on subsequent versions to ensure the product meets user expectations.
- Continuous Delivery and Feedback Loops: Lean Product Management advocates for shorter release cycles, enabling frequent product updates and enhancements based on user feedback and market trends. Gathering user feedback through various channels like surveys, customer support interactions, and analytics helps identify areas for improvement and informs future product iterations.
- Cross-functional Collaboration: Lean principles encourage close collaboration between designers, developers, and product managers to foster shared understanding and align efforts towards a common goal. Involving designers early in product development helps ensure a user-centred approach and facilitates the integration of design thinking principles.
The Role of Lean Product Managers
Lean Product Managers play a crucial role in driving the Lean Product Management process. They guide the product development journey, ensuring alignment with user needs, business goals, and market trends. Here are some key responsibilities of Lean Product Managers:
- Setting a Clear Product Vision: Lean Product Managers articulate a compelling product vision that aligns with the organization’s overall strategy. They define the product’s purpose, target audience, and key value propositions, guiding the team throughout the development process.
- Defining and Prioritizing User Needs: Lean Product Managers collaborate with stakeholders and conduct user research to understand the target audience’s pain points, goals, and desires. They distil this information into clear user personas and prioritize features and functionalities based on their potential impact and alignment with user needs.
- Facilitating Cross-functional Collaboration: Lean Product Managers foster a collaborative environment, bringing together designers, developers, and other team members to work towards a shared goal. They facilitate effective communication, coordinate efforts, and ensure that all stakeholders understand the product vision and objectives.
- Embracing Agile Principles: Lean Product Managers champion Agile methodologies like Scrum or Kanban to enable iterative development cycles and adaptive planning. They create and maintain a product backlog, continuously refine priorities based on user feedback, and collaborate closely with the development team to ensure the timely delivery of valuable features.
- Embracing Agile Principles: Lean Product Managers champion Agile methodologies like Scrum or Kanban to enable iterative development cycles and adaptive planning. They create and maintain a product backlog, continuously refine priorities based on user feedback, and collaborate closely with the development team to ensure the timely delivery of valuable features.
Benefits of LPM in Product Design
- Faster Time to Market: Lean practices help streamline the product development process, reducing wasteful activities and enabling faster delivery of valuable features to the market. By focusing on the essential user needs, teams can avoid over-engineering and accelerate the product’s time to market.
- Cost Optimization: Eliminating wasteful activities and maintaining a laser-sharp focus on user needs allows teams to optimize resource allocation and minimize unnecessary expenses. With continuous feedback loops, teams can prioritize features that bring the most value, maximizing the return on investment.
- Enhanced User Experience: By involving users throughout the product development lifecycle, Lean Product Management ensures that the end product aligns with their needs, preferences, and expectations. The iterative nature of Lean allows for rapid course correction and improvement, leading to a better user experience and higher customer satisfaction.
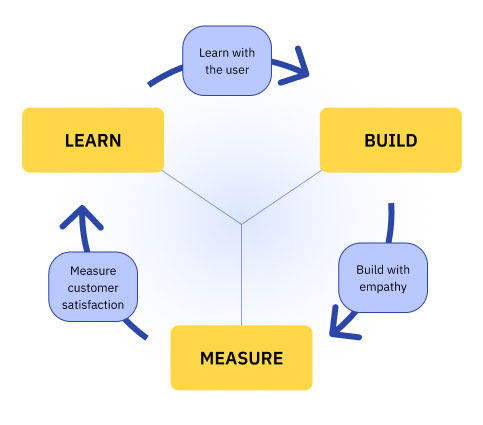
Lean Startup: A Complementary Approach to Lean Product Management
The Lean Startup methodology holds significant relevance within the realm of Lean Product Management. Developed by Eric Ries, the Lean Startup approach shares many principles with Lean Product Management and focuses on early-stage ventures and startups.
It complements Lean Product Management by providing a framework specifically tailored to the unique challenges faced by startups and early-stage ventures. By combining the principles of Lean Startup with Lean Product Management, organizations can optimize their product development process, reduce risk, and increase the likelihood of creating successful and sustainable products. Let’s explore the key aspects of the Lean Startup methodology:
- Build-Measure-Learn Feedback Loop: The Lean Startup methodology revolves around a continuous feedback loop known as the Build-Measure-Learn cycle. This iterative process emphasizes the rapid creation of Minimum Viable Products (MVPs) to test hypotheses and gather data from real users. The insights gained through measuring user behaviour and collecting feedback inform subsequent iterations and help refine the product.
- Validated Learning: Like Lean Product Management, the Lean Startup approach strongly emphasizes validated learning. It encourages entrepreneurs and product teams to approach their business hypotheses as experiments, seeking data-driven evidence to validate or invalidate assumptions. By adopting a scientific mindset, Lean Startup practitioners can minimize risks and make more informed decisions.
- Pivot and Persevere: The Lean Startup methodology recognizes that startups and early-stage ventures often need strategic adjustments. This concept is referred to as a “pivot.” A pivot involves changing one or more aspects of a product or business model based on insights gained from user feedback and market data. The Lean Startup methodology encourages entrepreneurs to be adaptable and resilient while pursuing their vision.
- Minimum Viable Product (MVP): The Lean Startup methodology shares the notion of developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) with Lean Product Management. An MVP represents the smallest product version that allows entrepreneurs to validate their assumptions and gather feedback. By focusing on the core features necessary to address user needs, startups can save time and resources while learning from real-world user interactions.
- Innovation Accounting: To effectively measure progress and evaluate the viability of a startup, Lean Startup advocates for the use of innovation accounting. Traditional financial metrics are often ill-suited to capture the unique challenges faced by early-stage ventures. Innovation accounting tracks relevant metrics, such as customer acquisition costs, user engagement, and retention rates. These metrics help entrepreneurs gauge the overall health and progress of their startups.
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
- Balancing Speed and Quality: The pursuit of speed can sometimes compromise quality. Implementing robust quality assurance processes, automated testing, and code reviews can help mitigate this risk.
- Overcoming Resistance to Change: Shifting to a Lean approach may encounter resistance from team members accustomed to traditional methodologies. Providing proper training, clear communication, and demonstrating the benefits of Lean can help alleviate concerns and gain buy-in.
- Prioritization and Scope Creep: Without effective prioritization, Lean projects can fall victim to scope creep. Regularly reassessing priorities, leveraging user feedback, and maintaining a well-defined product roadmap can prevent this.






