Brands that trust us
Introduction to Design Thinking
What is Design Thinking?
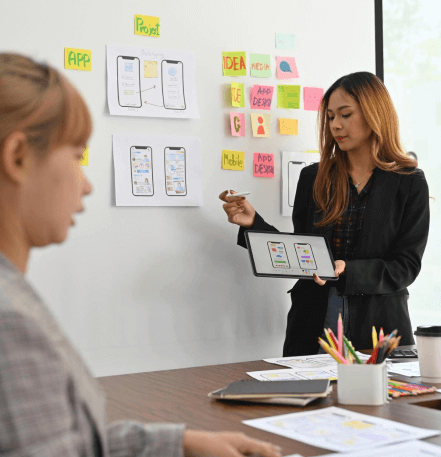
Design thinking is a human-centered approach to problem-solving that emphasizes empathy, creativity, and collaboration. It involves understanding user needs, generating ideas, prototyping solutions, and iterating based on feedback. By focusing on user experiences and iterative refinement, design thinking fosters innovation and creates solutions that truly resonate with people's needs and aspirations.
Application of Design Thinking in the Travel Industry

In the travel industry, design thinking is applied to enhance the overall customer experience by understanding travelers' needs, desires, and pain points.

It involves empathizing with travelers to uncover insights, ideating innovative solutions to address challenges such as booking processes, accommodation, transportation, and activities.

Prototyping and testing allow for refining solutions iteratively, leading to the creation of seamless and personalized travel experiences that delight customers and foster loyalty.

This approach encourages travel companies to continuously adapt and innovate to meet evolving customer expectations in a rapidly changing industry landscape.
Understanding the Traveler's Journey
Identifying Pain Points and Opportunities
In understanding the traveler's journey, identifying pain points and opportunities is crucial for crafting exceptional experiences. Here's how design thinking helps:

Empathize
Dive deep into travelers' emotions, needs, and motivations at every stage, from planning to post-trip reflections.

Define
Clearly define pain points such as cumbersome booking processes, lack of personalized recommendations, or difficulty navigating unfamiliar destinations.

Ideate
Generate creative solutions, like intuitive mobile apps for seamless bookings, virtual reality previews of accommodations, or personalized itineraries based on traveler preferences.

Prototype
Develop prototypes to test solutions and gather feedback, refining ideas iteratively to ensure they address identified pain points effectively.

Test
Conduct real-world tests to validate solutions, monitoring how they alleviate traveler frustrations and enhance overall experiences.
By doing this, businesses in the travel industry can innovate and tailor offerings to meet travelers’ needs more efficiently, fostering loyalty and satisfaction.
Mapping the Traveler's Experience
Mapping the traveler's experience is a pivotal step in leveraging design thinking to enhance the journey. Here's how to effectively map and analyze the traveler's experience
Define Stages
Identify key stages in the traveler's journey, from initial inspiration and research to booking, experiencing, and reflecting on the trip.
Capture Touchpoints
Map out all touchpoints where travelers interact with your brand or service, including website visits, social media engagement, customer service interactions, and on-site experiences.
Understand Emotions
Delve into the emotions and needs of travelers at each stage, recognizing moments of delight, frustration, excitement, and relaxation.
Identify Pain Points
Spot pain points and areas of friction that hinder the seamless flow of the traveler's experience, such as complicated booking processes, communication gaps, or unexpected disruptions.
Highlight Opportunities
Recognize opportunities to surprise and delight travelers, whether through personalized recommendations, seamless transitions between stages, or thoughtful gestures that exceed expectations.
Iterate and Refine
Continuously refine your understanding of the traveler's journey based on feedback, data analysis, and evolving customer preferences, ensuring your offerings remain relevant and impactful.
By meticulously mapping the traveler's experience and iteratively refining your approach, you can design more intuitive, personalized, and rewarding experiences.
Define: Defining Travel Challenges and Goals
Formulating Clear Objectives

In the realm of design thinking in travel, formulating clear objectives is the compass guiding our journey. Define the destination with precision, articulating goals that align with the needs and aspirations of both travelers and stakeholders. Embrace clarity as the cornerstone of innovation, distilling complex challenges into actionable targets.
Engage in collaborative ideation, weaving together diverse perspectives to craft objectives that resonate across teams. Emphasize measurability, setting key performance indicators (KPIs) that track progress and success.
With clear objectives as their North Star, businesses need to navigate the dynamic landscape of travel design, charting a course towards meaningful and impactful solutions.
Framing the Problem Statement

When it comes to design thinking in travel, framing the problem statement is akin to setting the stage for innovation. Delve deep into the heart of traveler challenges, distilling insights gleaned from user research into a concise and focused problem statement.

Illuminate the core issue at hand, shedding light on the pain points and aspirations of travelers and stakeholders alike. Embrace clarity and empathy as guiding principles, ensuring that the problem statement resonates with all involved.

Navigate the complexities of the travel landscape with precision, laying the groundwork for transformative solutions that address real-world needs. In framing the problem statement, we unlock the gateway to innovative design thinking in travel.
Ideate: Generating Innovative Solutions
Brainstorming Techniques
Brainstorming and ideation is important for the dynamic landscape of travel design thinking. Exploring innovative brainstorming techniques curated specifically for the challenges and opportunities within the travel industry helps bring diverse perspectives to the fore.
And immersive collaborative sessions where these diverse perspectives converge help brands to reimagine the travel experience.
Embracing techniques like destination mapping help chart pathways to innovative solutions that resonate with travelers' desires and needs.
When design thinking teams engage in experiential brainstorming, immersing themselves in the traveler's journey, it helps uncover insights that inspire transformative ideas. With these specialized techniques, brands can ignite the creative spark that propels them toward crafting unforgettable travel experiences.


Encouraging Creativity in Solution Generation
Unlock the boundless potential of design thinking in travel through strategies tailored to inspire creativity in solution generation. Cultivate a culture of innovation by encouraging diverse perspectives and fearless exploration.
Embrace unconventional thinking techniques such as role-playing, scenario mapping, and analogies to ignite fresh insights. Foster an environment where experimentation is celebrated and failure is embraced as a stepping stone to success.
Empower teams to think beyond the constraints of convention, drawing inspiration from diverse industries and disciplines. With creativity as their compass, travel businesses can chart a course towards transformative solutions that could possibly redefine the future of travel experiences.
Prototype: Designing Solutions
Rapid Prototyping Methods
Rapid prototyping methods play a crucial role in design thinking for travel, enabling quick iteration and validation of ideas to create innovative solutions tailored to travelers' needs.
Here are some rapid prototyping methods and their application in the context of travel:
Paper Prototyping
This method involves creating low-fidelity mock-ups of interfaces or experiences using paper and basic materials. In the travel industry, paper prototypes can be used to visualize and test user interfaces for booking systems, mobile apps, or in-flight entertainment systems.
Digital Prototyping Tools
Utilizing software tools such as Sketch, Adobe XD, or Figma, designers can create interactive prototypes of travel-related products or services. These digital prototypes allow for more detailed testing and refinement before investing in full-scale development.
Wizard of Oz Prototyping
In this method, a human "wizard" simulates the functionality of a proposed system behind the scenes while users interact with what appears to be a fully functional product. In the context of travel, this approach can be used to test new customer service processes or augmented reality features in hotel bookings.
Physical Prototyping
Creating tangible models or mock-ups of travel-related products or experiences can provide valuable insights into usability and aesthetics. For example, physical prototypes of new luggage designs or airport kiosks can be tested for ease of use and ergonomics.
Experience Prototyping
This method involves creating immersive, real-world simulations of travel experiences to understand user reactions and preferences. For instance, setting up a temporary pop-up hotel room to gather feedback on layout, amenities, and overall ambiance.
Co-creation Workshops
Hosting collaborative workshops with stakeholders and end-users to co-create prototypes can lead to more innovative solutions. Participants can use design thinking techniques like storyboarding or role-playing to generate and refine ideas for improving travel experiences.
By employing these rapid prototyping methods, design thinkers in the travel industry can gather feedback, create iterations accordingly, and consequently deliver solutions that address travelers’ evolving needs and expectations.
Testing and Iterating Prototypes
Testing and iterating prototypes are essential components of the design thinking process, especially in the context of travel, where user experience plays a critical role in the success of products and services.
Prototype Testing Methods
User Testing
Involves gathering feedback from actual users by observing their interactions with prototypes. For travel-related prototypes, this could include testing website navigation, booking flows, or the usability of mobile apps.
A/B Testing
Compares two or more versions of a prototype to determine which performs better in achieving specific goals. For instance, A/B testing could be used to compare different layouts for a hotel booking page to see which one leads to more conversions
Remote Usability Testing
Allows testers to provide feedback on prototypes from their own devices and locations. This method is particularly useful for testing travel-related apps or websites across different devices and network conditions.
Wizard of Oz Testing
Simulates the functionality of a prototype behind the scenes, allowing testers to interact with what appears to be a fully functional product. This method can be used to test new features or services in a controlled environment before full implementation.
Field Testing
Involves testing prototypes in real-world environments, such as airports, hotels, or tourist attractions. Field testing provides valuable insights into how prototypes perform in actual travel scenarios and allows for immediate user feedback.
Iterating Prototypes

Gather Feedback
Collect feedback from prototype testing sessions, user surveys, and other sources to identify areas for improvement.

Prioritize Changes
Analyze feedback to prioritize which aspects of the prototype need to be refined or redesigned first based on user needs and business objectives.

Iterate Quickly
Make iterative changes to the prototype based on feedback, focusing on addressing specific pain points or enhancing user experience.

Test Again
Once changes have been made, conduct additional rounds of testing to validate improvements and gather further feedback for iteration.

Continuous Improvement
Embrace a culture of continuous improvement by regularly testing and iterating prototypes throughout the design process, even after product launch, to ensure ongoing optimization and innovation.
In travel design thinking, testing and iterating prototypes helps businesses identify and address usability issues, refine features based on user preferences, and deliver products and services that meet travelers’ evolving needs.
Test: Validating Solutions
Continuous Improvement
User testing is a pivotal stage in the design thinking process for travel, ensuring that solutions are validated and optimized to meet the needs of travelers effectively. Here's a breakdown of how to conduct user testing within the context of travel
Define Testing Goals
Clearly outline the objectives of the user testing phase. Determine what aspects of the travel experience you want to evaluate, whether it's the usability of a booking platform, the effectiveness of a mobile app feature, or the overall satisfaction with a travel itinerary.
Recruit Diverse Participants
Select a diverse group of test participants who represent your target audience in the travel industry. This may include frequent travelers, families, solo adventurers, or business travelers. Aim for a mix of demographics, travel preferences, and experience levels to capture comprehensive feedback.
Develop Test Scenarios
Create realistic scenarios or tasks that mirror common user journeys within the travel domain. For instance, ask participants to search and book a flight, plan an itinerary, or navigate through a hotel booking process. Ensure that the tasks align with the objectives of the user testing phase.
Choose Testing Methods
Select appropriate testing methods based on your goals and resources. This may include in-person usability testing, remote testing, A/B testing, or moderated interviews. Consider the strengths and limitations of each method and choose the one that best suits your needs.
Iterative Improvement
Develop prototypes, mock-ups, or interactive simulations that represent the travel solutions being tested. This could involve wireframes, clickable prototypes, or fully functional prototypes depending on the stage of development. Ensure that the test materials accurately reflect the intended user experience.
Conduct Testing Sessions
Schedule and facilitate user testing sessions with selected participants. Provide clear instructions and guidance on how to complete the assigned tasks. Encourage participants to think aloud and express their thoughts and feelings as they interact with the prototypes.
Gather Feedback
Observe participants' interactions with the prototypes and take note of any usability issues, confusion points, or areas of improvement. Record qualitative feedback, such as verbal comments, observations, and suggestions for enhancement.
Analyze and Iterate
Analyze the feedback collected from user testing sessions to identify patterns and insights. Prioritize issues based on their impact on the user experience and iterate on the design accordingly. Make necessary adjustments to address usability issues, improve functionality, or enhance the overall user experience.
Repeat and Refine
Iterate on the design based on the insights gained from user testing, and conduct additional rounds of testing as needed. Continuously refine the prototypes until they meet the desired level of usability and effectiveness in solving travelers' needs.
By conducting user testing in the design thinking process for travel, you can ensure that solutions are thoroughly validated and optimized to deliver exceptional experiences for travelers.
Gathering Feedback for Iteration

In design thinking for travel, gathering feedback for iteration is paramount to refining solutions that truly resonate with travelers. Engage stakeholders and end-users through various channels, such as user testing sessions, surveys, and feedback forms, to collect valuable insights.

Listen attentively to their experiences, preferences, and pain points, identifying areas for improvement and innovation. Analyze feedback with a keen eye, discerning patterns and prioritizing enhancements based on their impact on the travel experience.

Iteratively refine prototypes, services, and experiences, incorporating feedback to ensure they meet the evolving needs and expectations of travelers on their journey.
Implementation and Beyond
Strategies for Implementation in Travel Services
Implementing design thinking strategies in travel services requires a holistic approach that prioritizes user needs, fosters innovation, and drives meaningful change.
User-Centric Approach
Place travelers at the center of service design by understanding their motivations, pain points, and preferences. Conduct thorough user research, including interviews, surveys, and observation, to gain deep insights into travelers' needs throughout their journey.
Empathy Mapping
Develop empathy maps to visualize and understand the emotions, thoughts, and behaviors of travelers at various touchpoints. Use empathy maps to identify opportunities for enhancing the travel experience and addressing pain points effectively.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Foster collaboration between multidisciplinary teams, including designers, marketers, engineers, and customer service representatives. Encourage diverse perspectives and expertise to generate innovative solutions that address both business goals and user needs.
Iterative Prototyping
Adopt an iterative approach to prototyping, continuously refining and testing solutions based on user feedback. Create low-fidelity prototypes early in the design process to gather feedback quickly and iterate rapidly towards a final solution.
Co-Creation Workshops
Organize co-creation workshops with stakeholders and end-users to ideate and prototype solutions collaboratively. Leverage design thinking methods such as brainstorming, storyboarding, and role-playing to generate innovative ideas and gain buy-in from all stakeholders.
Service Blueprinting
Develop service blueprints to visualize the end-to-end travel service journey, including all touchpoints, channels, and interactions. Use service blueprints to identify pain points, bottlenecks, and opportunities for improvement across the entire service ecosystem.
Digital Innovation
Embrace digital innovation to enhance the travel experience through technology-driven solutions. Explore opportunities such as mobile apps, artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and augmented reality to personalize services, streamline processes, and create immersive experiences for travelers.
Continuous Improvement
Cultivate a culture of continuous improvement by soliciting feedback from travelers regularly and iteratively refining services based on their evolving needs and preferences. Implement feedback loops to capture insights from customer interactions and use data analytics to inform decision-making.
Design Thinking Training
Invest in design thinking training and education for employees across the organization to build empathy, creativity, and problem-solving skills. Empower teams to apply design thinking principles in their day-to-day work and drive innovation at every level of the organization.
Measuring Impact
Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of design thinking initiatives on business outcomes and customer satisfaction. Track metrics such as customer retention, Net Promoter Score (NPS), and conversion rates to gauge the effectiveness of implemented solutions.
By adopting these strategies, travel services can leverage design thinking principles to create exceptional experiences for travelers, drive business growth, and stay ahead in a competitive market landscape.
Scaling Successful Solutions
Scaling successful solutions in the context of design thinking for travel involves expanding and replicating effective strategies, processes, and innovations across different regions, markets, or segments within the travel industry.
Here's how travel businesses can effectively scale successful solutions:
Document Best Practices
Start by documenting successful solutions, including the design thinking methodologies, processes, and outcomes achieved. Capture key learnings, insights, and success stories to create a knowledge repository that can be shared and leveraged across the organization.
Standardize Processes
Standardize design thinking processes and methodologies to ensure consistency and alignment across different teams, departments, or locations. Develop clear guidelines, templates, and tools to facilitate the implementation of design thinking practices at scale.
Train and Empower Teams
Provide comprehensive training and resources to empower teams at all levels to apply design thinking principles effectively. Offer workshops, seminars, and online courses to build empathy, creativity, and problem-solving skills among employees.
Create Cross-Functional Teams
Foster collaboration and innovation by forming cross-functional teams that bring together diverse perspectives and expertise from different areas of the organization.
Adapt to Local Contexts
Tailor successful solutions to suit the unique needs, preferences, and cultural nuances of different regions, markets, or customer segments within the travel industry. Adapt design thinking methodologies and solutions to local contexts while maintaining alignment with overarching business objectives.
Adapt to Local Contexts
Tailor successful solutions to suit the unique needs, preferences, and cultural nuances of different regions, markets, or customer segments within the travel industry. Adapt design thinking methodologies and solutions to local contexts while maintaining alignment with overarching business objectives.
Pilot and Iterate
Pilot successful solutions in new markets or segments to test their effectiveness and gather feedback for iteration.
Leverage Technology
Utilize technology to streamline and automate processes, facilitate collaboration, and scale successful solutions efficiently. Explore digital tools, platforms, and applications that support design thinking practices.
Measure Impact and Iterate
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of scaled solutions on business outcomes, customer satisfaction, and innovation effectiveness.
Promote a Culture of Innovation
Foster a culture of innovation and continuous improvement by recognizing and rewarding experimentation, creativity, and risk-taking. Encourage employees to challenge the status quo, share ideas, and contribute to the evolution of successful solutions over time.
Collaborate with Partners
Collaborate with external partners, such as industry associations, academic institutions, startups, and technology vendors, to access new perspectives, capabilities, and resources for scaling successful solutions.
By following these strategies, organizations can effectively scale successful solutions derived from design thinking practices.